What Are Skills? Complete Guide to AI Agent Skills | 2026

Learn what Skills are for AI agents, Skills vs Prompts vs MCP differences, how to write Skills, and how to install and use them. Includes real-world examples.
If you've been in AI circles lately, you've probably seen one word everywhere: Skills.
The recent explosion of OpenClaw has brought Skills into the mainstream spotlight. GitHub repositories about Skills are getting 18K+ stars. Projects like Superpowers are building entire development workflows around them. The excitement around Skills rivals the Prompt craze of 2023-2024.
So what exactly are Skills? How are they different from Prompts and MCP? And most importantly—how do you actually use them?
What Are Skills?
The Origin Story
Skills launched in October 2025 as a feature in Claude Code by Anthropic. The real explosion happened on December 18 when Anthropic opened Skills as a standard, making it available for everyone to adopt.
Today, Skills work across multiple platforms:
- Claude Code (official)
- OpenCode
- Codex
- Cursor
- Codebuddy
- OpenClaw
- Any AI Agent...
What Exactly Are Skills?
Skills, literally translated, means "capabilities" or "abilities." In the context of AI agents, Skills are reusable capability packages designed specifically for agents to use.
Think of Skills as giving an agent a professional handbook. When the agent needs to perform a specific task—like creating a presentation, processing data, or generating reports—it can pull up the relevant Skill and follow its instructions to execute the work accurately and consistently.
Skills Are Folders, Not Just Text
Here's the key difference from traditional Prompts: Prompts are just text in a markdown file. Skills are complete folders containing multiple files and resources:
my-skill/ # Skill name
├── SKILL.md # Core file (required)
├── reference.md # Reference docs (optional)
├── examples.md # Examples (optional)
├── scripts/ # Scripts directory (optional)
└── helper.py # Python script
Skills vs Prompts vs MCP - The Real Differences
Many people confuse Skills with Prompts or MCP. Let's clarify what each one actually does:
Skills = Reusable Capability Packages
Skills are structured knowledge packages that agents can reference and execute repeatedly. They contain instructions, workflows, scripts, and documentation that teach an agent how to perform specific tasks consistently.
Key characteristics:
- Reusable and persistent across all conversations
- Contains structured knowledge and workflows
- Loads progressively when needed
- Transforms procedural knowledge into callable capabilities
- Works like an operational manual the agent consults
Prompts = One-Time Instructions
Prompts are natural language commands you give to an AI in a specific conversation. They're temporary directives that only exist in the current session.
Key characteristics:
- One-time, temporary commands
- Natural language instructions
- Only exists in the current conversation
- Disappears when the conversation ends
- Perfect for ad-hoc, reactive tasks
MCP (Model Context Protocol) = System Access
MCP doesn't teach the agent anything. It provides connections and permissions to external systems—databases, APIs, file systems, and third-party tools.
Key characteristics:
- Enables safe connections to external systems
- Manages permissions and access rights
- Handles API integrations
- Not about teaching capabilities, but enabling access
- Functions as an authentication and connection layer
Quick Comparison Table
Feature | Skills | Prompts | MCP |
Designed For | AI Agents | AI Models (any) | AI Applications |
Purpose | Teach workflows | Give instructions | Grant access |
Persistence | Permanent, reusable | Temporary, single-use | Permanent connections |
Scope | Knowledge & procedures | Specific commands | External systems |
Format | Folder with multiple files | Text-based message | Protocol/API |
Use Case | Standardized tasks | Ad-hoc requests | System integration |
Why Skills Matter
Skills Are Like Workflows, But Better
Notice how the examples feel like workflows? That's intentional. Agent + Skills can replicate almost any workflow-based AI task. In fact, one experienced developer stated: 'Almost all AI tasks that can be completed with workflows can be achieved with Agent + Skills.'
The difference? Skills offer more flexibility, adaptability, and natural language interaction compared to rigid workflow systems.
The Underestimated Potential
Skills remain significantly undervalued. Whether you're a professional packaging expertise into reusable workflows, or a beginner automating repetitive needs, Skills offer tremendous potential.
- For professionals: Encapsulate your experience and workflows into Skills that maintain quality and consistency
- For regular users: Package repetitive tasks once, then call them indefinitely
- For everyone: Reusability is the core value proposition
The Compound Effect
The true power of Skills emerges through accumulation:
- Your first Skill: The moment it runs successfully, you understand the value
- Your second Skill: You start seeing patterns and possibilities
- Your Skill library: You enter a state of creative freedom
At that stage, automation isn't a feature—it's your new operating system.
How to Write Skills
File Structure
A complete Skill is organized as a folder with the following structure:
my-skill/
├── SKILL.md # Required - Core instructions
├── reference.md # Optional - Reference docs
├── examples.md # Optional - Usage examples
├── templates/ # Optional - Template files
└── scripts/ # Optional - Utility scripts
└── helper.py
The SKILL.md File Format
SKILL.md is the core file with a fixed two-part structure:
Part 1 - YAML Header (Required)
yaml
---
name: Your skill name
description: Brief description of functionality and when to use it
---
This metadata helps agents discover and understand when to use the Skill.
Part 2 - Markdown Body (Required)
markdown
# Your Skill Name
## Instructions
Clear, step-by-step operational guidelines for the agent.
## Examples
Concrete code or operation examples showing how to use this skill.
## Output Format
Expected output structure and requirements.
## Best Practices
Tips and conventions for optimal results.
Naming Rules
Folder naming is strict:
- Lowercase letters only
- Hyphen separators
- No spaces or uppercase letters
Examples:
- ✅ Correct:
hotspot-collector - ❌ Wrong:
Hotspot_Collector - ❌ Wrong:
hotspot collector
Writing the Description Field
The description field is the most critical component. It determines when and how agents invoke your Skill.
Always use third person. The description gets injected into system prompts. Inconsistent perspectives cause errors.
Examples:
- ✅ Good: "Processes Excel files and generates reports"
- ❌ Bad: "I can help you process Excel files"
- ❌ Bad: "You can use this to process Excel files"
Include trigger keywords. Make it clear when this Skill should activate.
Content Best Practices
- Keep the entire SKILL.md under 500 lines for optimal performance
- Focus on clarity over comprehensiveness
- Provide concrete, actionable examples
- Structure content logically
How to Install Skills
Anthropic's Official Skills Repository
Anthropic maintains an official Skills repository with production-ready implementations. Access it at:
https://github.com/anthropics/skills
Recommended Skills for everyone:
- docx - Word document creation and editing
- xlsx - Spreadsheet manipulation
- pdf - PDF generation and processing
- pptx - Presentation creation
- frontend-design - UI/UX development
- skill-creator - Meta-skill for creating new Skills
Installation Method 1 - Command-Based
The simplest approach uses a natural language command. Here's how:
- Open Claude Code or OpenCode (this example uses OpenCode)
- Send this message to the agent:
'Install this skill, skill project address: https://github.com/anthropics/skills/tree/main/skills/skill-creator'
- Done. The Skill installs automatically.
To install other official Skills, simply replace the URL with the desired Skill's GitHub path.
Installation Method 2 - Manual Folder Installation
Alternatively, manually place Skill folders into your local directory:
Directory locations:
- Claude Code: ~/.claude/skills
- OpenCode: ~/.config/opencode/skill
Mac example: /Users/khazix/.config/opencode/skill
Windows example: C:\Users\YourUsername\.config\opencode\skill
Important notes:
- The skill folder doesn't exist initially—create it manually
- Global installation: Skills in these directories work across all projects
- OpenCode: Restart required after installation
- Claude Code: Version 2.1.0+ supports hot reload (no restart needed)
Recommendation: Use global directories for all Skills so they're accessible from any project directory. This maximizes convenience. Developers with specific organizational needs may choose different configurations.
How to Use Skills
It's Completely Automatic
Running Skills requires zero manual intervention. Simply converse naturally with OpenCode or Claude Code. The agent automatically:
- Analyzes your request
- Selects the appropriate Skill(s)
- Executes the workflow
No manual triggering. No special commands. Just describe what you need.
Typical Workflow Example: Amazon Competitor Analyzer
Let's walk through a real example using the Amazon Competitor Analyzer Skill:
Step 1: Install the Skill
Simply tell opencode or other agent to install it:
"Install this skill, skill project address: https://github.com/browser-act/skills/blob/main/amazon-competitor-analyzer/SKILL.md"
Done. The Skill installs automatically.
Step 2: Configure API (if needed)
Some Skills require external services. For this Skill, you need a BrowserAct API key.
To get your API key:
- Log in to BrowserAct at browseract.com
- Navigate to Integrations & API in the left sidebar
- Click API Keys tab
- Copy your existing API key or create a new one
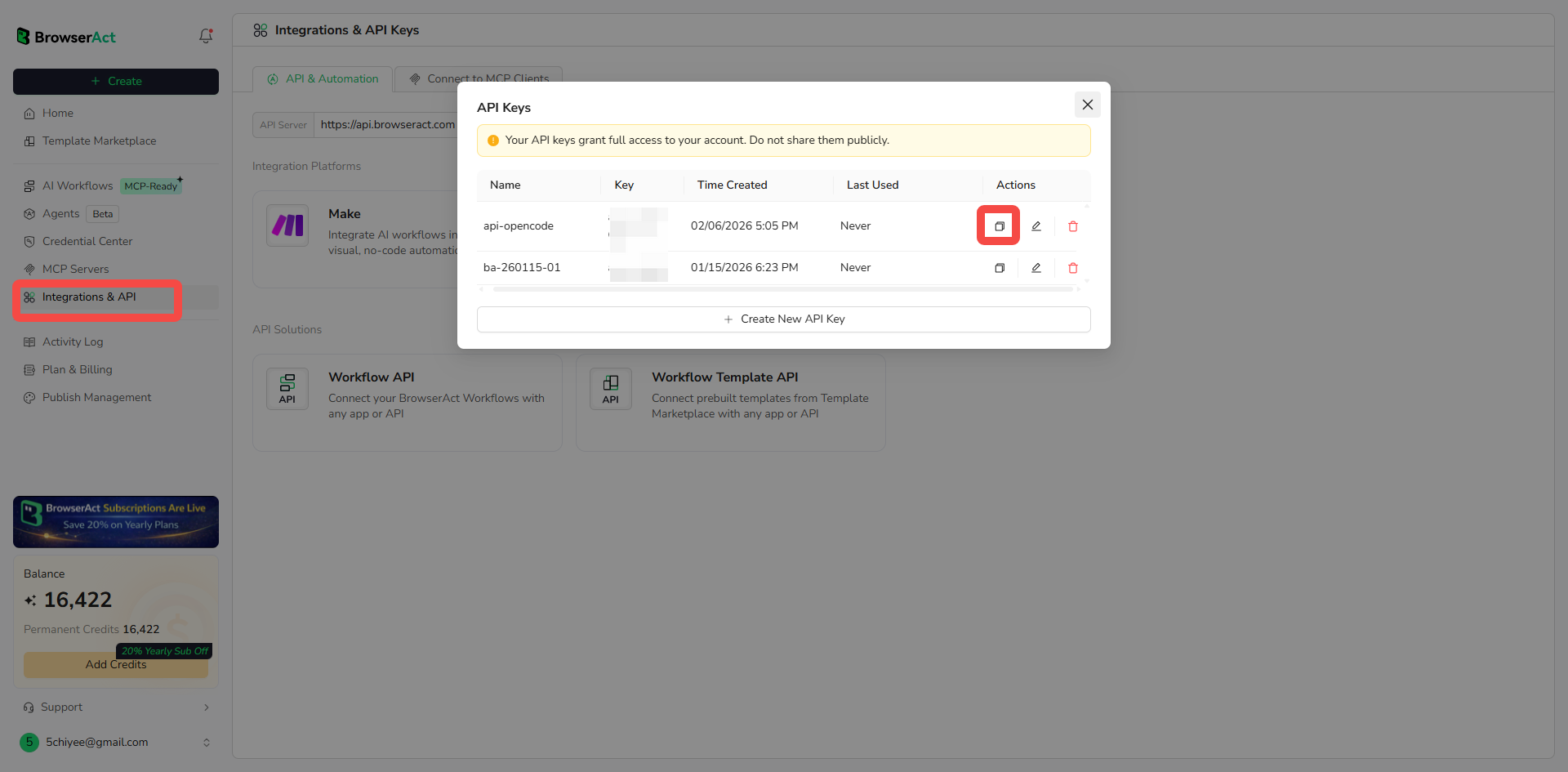
Then configure it in your terminal:
"export BROWSERACT_API_KEY="your-api-key""
Step 3: Start Using Through Conversation
Simply talk to the agent naturally. Here are some example requests:
- Basic analysis: "Analyze the following Amazon ASIN: B09G9GB4MG"
- Compare multiple products: "Compare these three products: B07ABC11111, B07DEF22222, B07GHI33333"
- Deep specification analysis: "Analyze the technical specification differences: B09G9GB4MG, B09ABC11111"
- Complete competitive landscape: "Analyze competitor landscape: B09G9GB4MG, B07DEF22222, B07GHI33333, B09JKL44444"
What Happens Behind the Scenes
The Skill automatically:
- Extracts product data via BrowserAct API
- Analyzes specifications, reviews, and visual strategies
- Identifies competitor moats and vulnerabilities
- Generates structured reports (JSON, CSV, Markdown)
The process feels conversational because it is. Skills operate behind the scenes, seamlessly integrated into the agent's capabilities.
Ready to try it yourself? Sign up for a free BrowserAct account, grab your API key, and start analyzing Amazon competitors in minutes.
Get Started Today
The best way to understand Skills isn't reading about them—it's building one. Here's your action plan:
- Install the skill-creator Skill using either installation method above
- Identify ONE repetitive task you do regularly:
- Screening trending topics
- Analyzing competitor products
- Summarizing articles or links
- Extracting data from websites
- Formatting and processing data
- Create your first Skill to automate that task
- Run it and experience the moment it works
- Feel the power of reusability
After completing your first Skill, you'll immediately start thinking about the second one. Then the third. Eventually, you'll want to systematize all your repetitive processes.
That progression leads to a transformative state: freedom to create rather than execute.
Conclusion
Skills represent a fundamental shift in how we work with AI agents. Instead of giving constant instructions, you create reusable capability packages. The agent references them independently, executes reliably, and iterates autonomously. You say less. They deliver more.
For web automation tasks—competitor analysis, data extraction, monitoring—Skills become even more powerful when combined with tools like BrowserAct. The Amazon Competitor Analyzer we showed earlier demonstrates this: reusable workflows plus browser automation.
Start analyzing your competitors today. Install skill-creator and package one repetitive task. Screen trends, analyze competitors, or transform data—pick one and build it.
When it runs successfully, you'll understand: Skills are about reusability.
Tomorrow you'll build your second Skill. The day after, your third. Eventually, you'll systematize everything.
Relative Resources

AI Agents' Social Revolution: OpenClaw + Moltbook Explained

OpenClaw Skills: 8 Case Studies Transforming Work in 2026

OpenClaw Becomes Boss: AI Hiring Humans via RentAHuman.ai

How to Set Up OpenClaw: Your Personal AI Assistant
Latest Resources

10 Killer AI Agent Skills That Are Dominating GitHub Now

How One Person Made $100K in 3 Days Selling OpenClaw Setups

Amazon Price Scraper: Monitor Competitor Pricing in Real-Time | No Coding Required