
Automated Content Translation
Brief
🎯 Core Function: Automated Extraction, Structuring, and Expert Translation of Technical Content
This workflow is designed for organizations that need to quickly and accurately localize complex technical articles (like software tutorials, developer documentation, or API guides). It uses BrowserAct to intelligently separate text and code blocks from a source URL, Gemini AI for a two-stage process (reconstruction then expert translation), and Make.com to manage the pipeline and store the final localized content in Google Sheets.
Part 1: BrowserAct Workflow Description
This core module handles the specialized extraction of raw, semi-structured components from the source article:
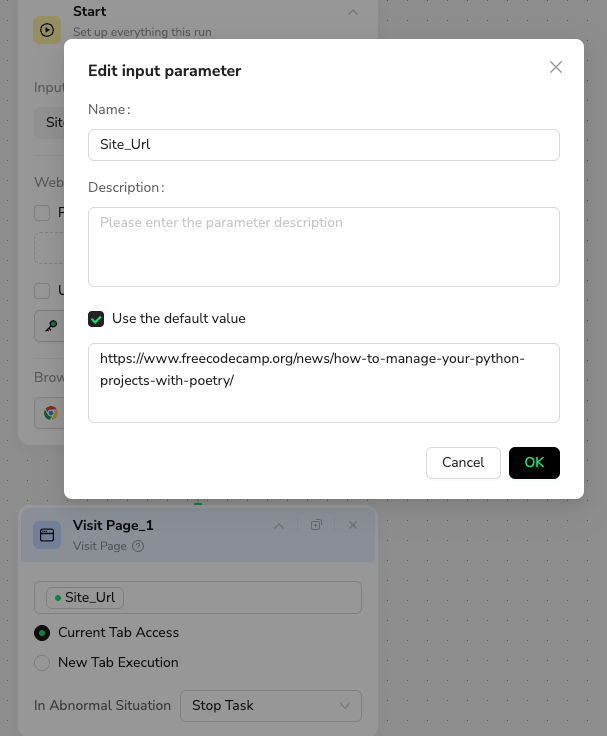
Target URL Input: The workflow is designed to visit a predefined, single URL (which can be easily modified by the user).
Intelligent Component Extraction:
The Agent visits the specified URL.
It uses advanced extraction techniques to capture all key components of the technical article, separating them based on their function:
Title and Lede (Introduction)
Body Text (Narrative content, often containing embedded formatting cues like underlines for headers)
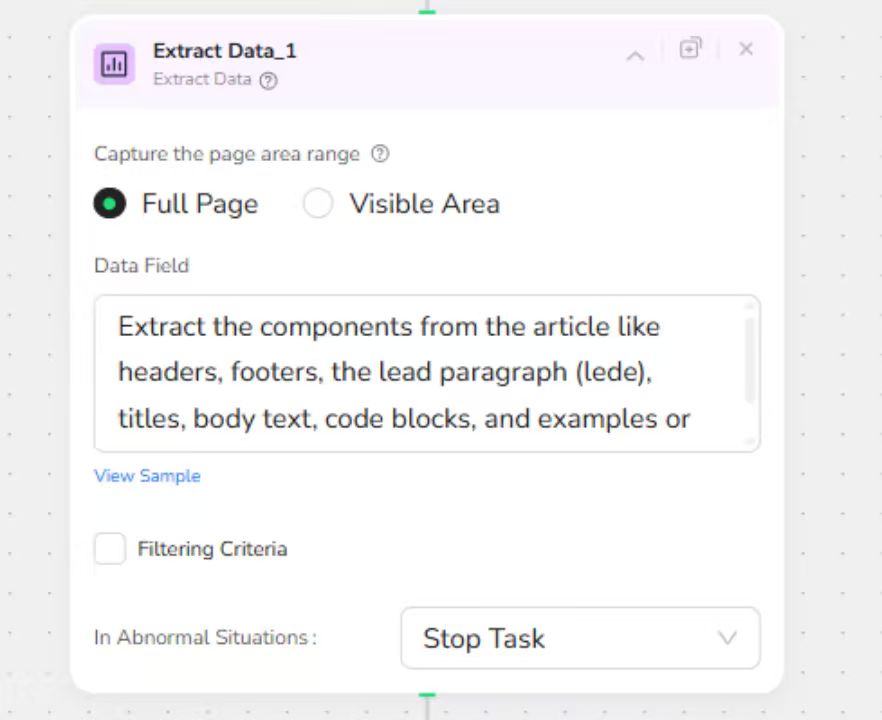
Code Blocks (Raw code snippets, separated from the narrative)
Data Consolidation: The extracted data is organized into a single, comprehensive JSON object that serves as the input for the AI's reconstruction stage.
Part 2: Automation Integration with Make.com
The Make.com scenario executes the multi-stage AI processing necessary for expert localization:
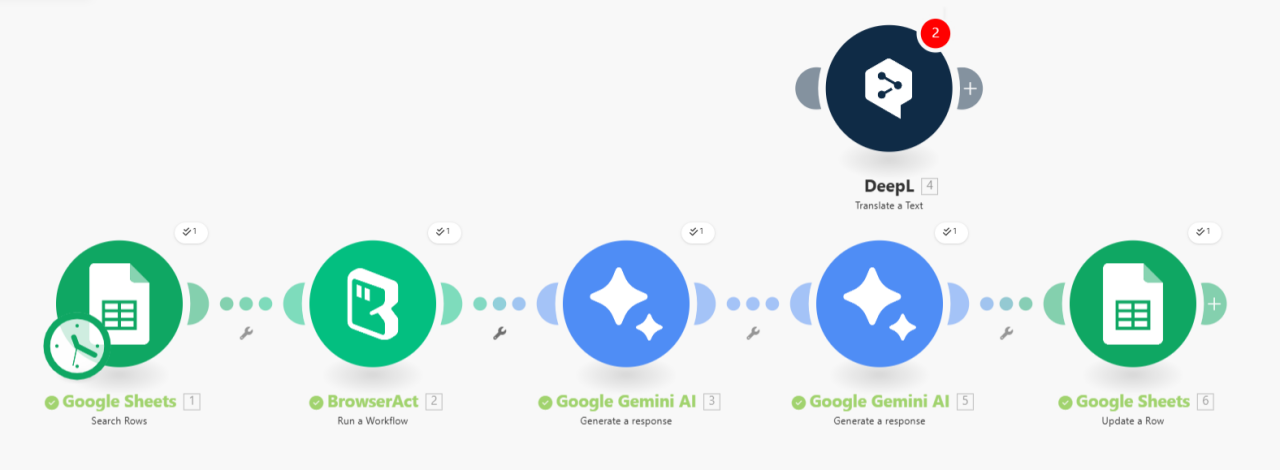
Trigger & Scraping:
The workflow can be triggered by a list of URLs from Google Sheets (or a manual trigger).
The URL is sent to the BrowserAct node to perform the component extraction.
AI Stage 1: Technical Editor & Reconstruction (Gemini/Prompt 1):
The raw, separated JSON components are sent to the first AI node.
Acting as an Expert Technical Editor, the AI's task is to:
Structure: Convert raw text headers (like underlined text) into proper Markdown headers (H1, H2).
Code Injection: Crucially, it logically maps and injects the raw code snippets (from the code_block field) into the correct chronological location within the narrative text, formatting them with language-specific triple backticks (```).
This stage results in a single, perfectly formatted Markdown article in the source language.
AI Stage 2: Expert Translation (Gemini/Prompt 2 or DeepL):
The reconstructed source article is sent to the second node (Gemini or a dedicated translation tool like DeepL).
Acting as an Expert Technical Translator, the AI meticulously translates the content from the source to the target language (e.g., English to Spanish), following strict rules:
Preserve Integrity: Technical terms, file names (pyproject.toml), and all code within code blocks are never translated.
Maintain Formatting: Exact Markdown structure (headers, bullets) is preserved.
Final Storage:
The final, fully translated and formatted article (in Markdown) is stored in the Google Sheet, ready for publishing or review.
✨ Applicable Scenarios (Use Cases)
Developer Documentation Localization: Instantly translate API guides, SDK documentation, and tutorials into multiple languages, ensuring code blocks remain untouched and functional.
Global Content Strategy: Automate the process of launching technical blog posts simultaneously across international markets.
Content Team Efficiency: Significantly reduce the manual labor and QA time required for translating technical content by separating the editorial and translation tasks into two automated, specialized AI stages.
Educational Resource Translation: Quickly localize coding or software engineering courses and articles for a global student base.
