
Travel Deal Hunter
Brief
✈️ Travel Deal Hunter – Core Function: Automated Flight Deal Discovery and Delivery
This workflow turns a Telegram conversation into an end-to-end flight search experience. A user messages a Telegram bot with their trip details, the system validates and parses the intent with Gemini AI, triggers a BrowserAct workflow to search flights on a live website, and finally formats the best deals into a rich HTML message sent back to Telegram. It combines BrowserAct for on-page automation and scraping, Make.com for orchestration and routing, and Gemini AI for both intent parsing and high quality message formatting.
🌐 Part 1: BrowserAct Workflow Description
This BrowserAct module is responsible for navigating the travel website, entering search parameters, handling popups, and extracting structured flight data that can be consumed by Make.com and Gemini.
Start Node and Dynamic Input Parameters
The workflow begins with a Start node that defines the dynamic input parameters used for each run. These parameters are designed to be injected from Make.com so that every search can use different origins, destinations, and dates.
The defined inputs are:
Travels – the base URL of the flight search site (for example https://www.google.com/travel/flights)
Origin – the departure city or airport
Destination – the arrival city or airport
DepartureDate – outbound date
ReturnDate – return date, which can be left empty for one-way trips
The Start node also includes optional Website Auto-Login settings and browser configuration, but for this workflow the key is that all travel details are externalized via parameters.
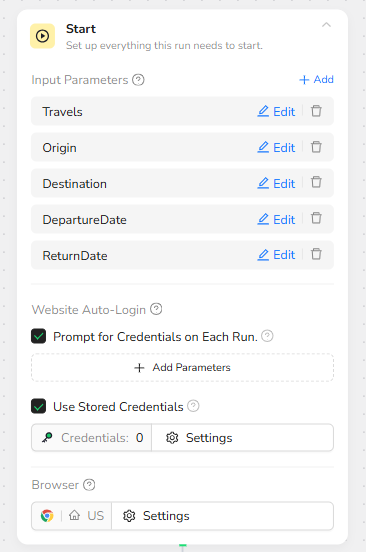
Visit Travel Page
After initialization, BrowserAct opens the travel site specified in the Travels parameter. The Visit Page node receives the Travels input and loads it in the current browser tab. If something goes wrong (for example the page fails to load), the node is configured to stop the task in abnormal situations, making failures explicit rather than silent.
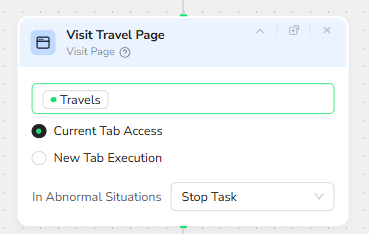
Popup Detection and Cleanup
Many travel or booking sites show popups such as cookie banners, promotions, or login prompts that can block form fields. To keep the interaction reliable, the workflow introduces a Condition node that asks: “Is any popup visible?”
If the condition returns True, execution flows into a Close Popup node. This node targets the popup close element and clicks it, clearing the screen. If the condition is False, the workflow simply continues without attempting to close anything. In both paths, abnormal situations are set to Stop Task to prevent the robot from blindly clicking on a changed layout.
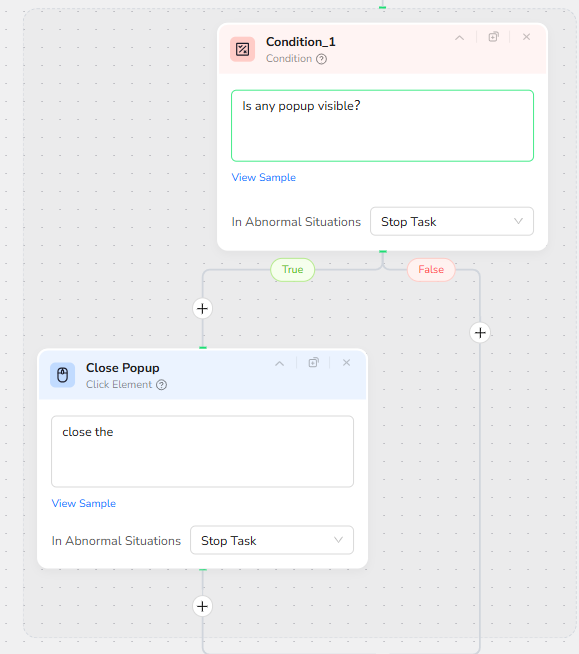
Filling in Destination and Origin
Next, the workflow begins populating the search form. Two Input Text nodes handle the destination and origin fields in order.
The Input Destination node targets the “Where to?” text field, identified as the first input field. The text to input is bound to the Destination parameter. The node is configured to press Enter after typing, helping the page validate or autocomplete the entry.
Immediately after, the Input Origin node targets the “Where From?” field, described as the second input field from the left. It injects the Origin parameter and again presses Enter after typing, ensuring the interface recognizes the value.
Both nodes are configured to Stop Task in abnormal situations, which provides strict error handling if the UI changes and the fields cannot be located.
Filling in Departure and Return Dates
Once locations are set, the workflow enters the travel dates. Two more Input Text nodes handle this step.
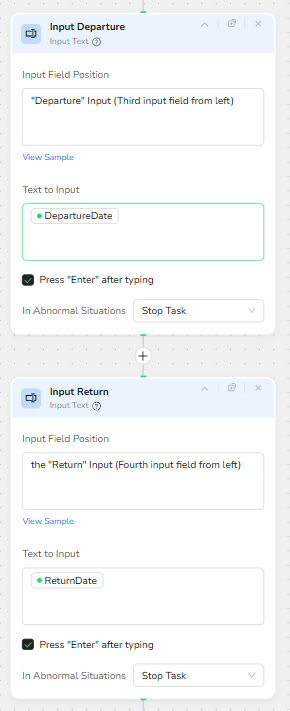
The Input Departure node targets the “Departure” input, identified as the third input field. It receives the DepartureDate parameter as its text input and triggers Enter after typing, allowing the page’s date parsing logic to run.
Next, the Input Return node targets the “Return” input, identified as the fourth input field. It receives the ReturnDate parameter, also followed by Enter. If ReturnDate is left empty for a one-way trip, the behavior depends on how the website handles empty or default values, but structurally the workflow keeps the same sequence.
Both date input nodes share the same robust error handling configuration as the previous steps, stopping the task if an abnormal situation occurs.
Triggering the Search Action
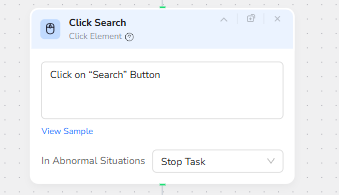
With all the form fields filled, the workflow needs to initiate the search. A Click Element node named Click Search is configured to click on the site’s “Search” button. This node is the turning point from setup to results: once clicked, the website loads the list of available flights based on the parameters supplied.
Again, the node is set to Stop Task on errors, ensuring that if the “Search” button is not found or its selector changes, the issue is surfaced instead of silently failing.
Extracting Structured Flight Data
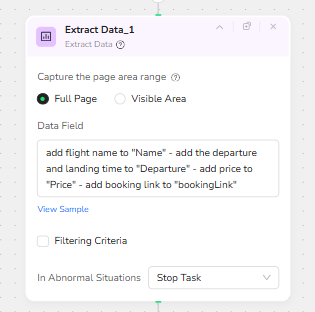
After the search results are loaded, the workflow performs a full page extraction of the flight listings. The Extract Data node is configured to capture data across the full page rather than a limited viewport, making it more resilient to different screen sizes or scroll positions.
The Data Field instructions describe how the information should be mapped into structured fields:
Flight name goes into “Name”
Departure and landing time go into “Departure”
Price goes into “Price”
The booking link goes into “bookingLink”
This configuration lets BrowserAct return an array of flight objects in JSON format, each object containing the core attributes needed for ranking and display. This is the primary output that later steps in Make.com will consume and transform.
🤖 Part 2: Automation Integration with Make.com
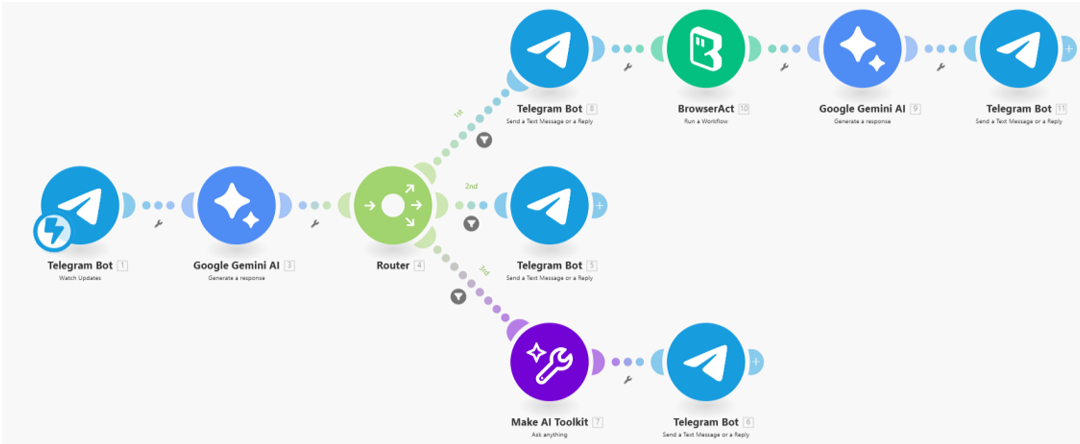
Make.com coordinates the full conversational automation, connecting Telegram, Gemini AI, and BrowserAct into one seamless interaction. The process begins when the Telegram bot receives a user message. This text is passed into Gemini AI, which determines whether the user has provided complete flight details, incomplete information, or is simply engaging in casual chat.
A Router then directs the flow into one of three efficient paths.
If the message contains complete travel details, Make.com injects all parameters into BrowserAct, triggering a live flight search. The extracted JSON is then passed back into Gemini, which formats the cheapest flight deals into a clean HTML message and sends it directly to Telegram.
If the user intends to search but hasn’t supplied all required information, Make.com replies with a simple clarification message guiding them to provide Origin, Destination, Departure, and Return in one line.
If the message is general conversation rather than a flight request, a lightweight AI response module generates a friendly reply to keep the interaction natural.
Through this structure, Make.com ensures that BrowserAct only runs when needed, user intent is always correctly interpreted, and results are delivered in a polished, human-friendly format.
✨ Applicable Scenarios and Use Cases
Personal Flight Deal Assistant
Users can message the Telegram bot with natural language trip requests such as “LAX to JFK on March 3, back March 8”. The system understands the intent, searches live prices via BrowserAct, and returns a curated list of the cheapest options, all without leaving the chat.
Travel Agency Customer Frontline
Agencies can embed this bot into their customer communication channels. Agents or customers type trip details into Telegram, and the workflow instantly provides sorted options, which human agents can then refine or book. This reduces manual website browsing and speeds up the quoting process.
Deal-Hunting Communities and Channels
Community owners can run the Telegram bot inside a group or channel where members frequently ask for deal checks. The scenario can return formatted, clickable deal lists that members can act on immediately.
Internal Tools for Frequent Travelers or Corporate Travel Teams
Companies with frequent travelers can integrate this workflow into internal bots to quickly evaluate price options when planning trips, making it easier to compare rough budgets before going into a formal booking process.
Through the combination of intent detection, robust browser automation, structured data extraction, and polished HTML formatting, Travel Deal Hunter delivers an end-to-end experience that feels like chatting with an intelligent travel concierge while relying on live data from real flight search sites.
