
Smart Lead Finder & Suggestion Bot
Brief
💼 Core Function: Smart Lead Finder & Suggestion Bot
This workflow turns a Telegram chat into an on-demand lead finder for local service providers. When a user types a natural language request such as “My toilet is not working in Brooklyn, NY, can you call someone?”, the automation understands the message, extracts the service and location, uses BrowserAct to search Google Maps, formats the results with Gemini AI, and sends a rich, HTML-styled list of providers back to Telegram in seconds.
It is built from two cooperating layers: a BrowserAct workflow that performs live Google Maps scraping, and a Make.com scenario that handles intent detection, routing, AI formatting, and Telegram delivery.
🧠 Part 1: BrowserAct Workflow Description
Input Parameters and Run Configuration
The BrowserAct workflow is designed around three global input parameters that Make.com can inject on every run:
GoogleMap_Search holds the location context, such as a city or neighborhood (for example “Brooklyn, NY”).
Service holds the type of provider the user is looking for (for example “Plumber” or “Electrician”).
Extracted_Data controls the target number of business listings to collect before the workflow stops looping.
With these three parameters, the same BrowserAct workflow can be reused for any combination of service and location without modification.
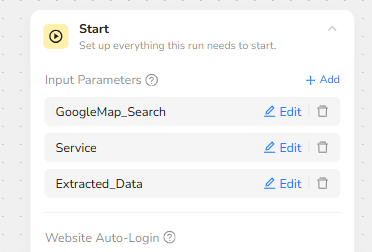
Google Maps Navigation and Dynamic Search
The Visit Page node uses the dynamic values GoogleMap_Search and Service together as the search phrase. Instead of hard-coding a URL, the agent opens Google Maps and types a combined query such as “Brooklyn, NY Plumber” into the search interface.
The node is configured to run in the current browser tab and to stop the task in abnormal situations, ensuring the run is cleanly terminated if the page fails to load or the site layout changes unexpectedly.
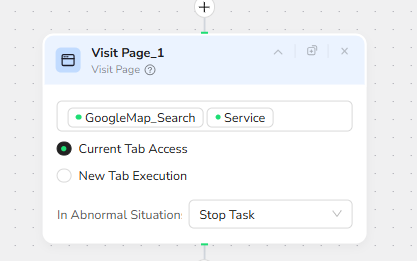
Loop Control: Stop When Enough Leads Are Collected
A Loop node governs how many pages of the Google Maps results are processed. Its stop condition references the Extracted_Data input parameter and reads conceptually as “continue looping until the number of extracted records equals Extracted_Data.”
This allows a flexible “up to N leads” behavior. If Extracted_Data is set to 10, the workflow will continue to cycle through extraction and scrolling until 10 unique businesses have been captured or until a safety cap is reached.
The node also sets Max Duration number of cycles to 10 and specifies Stop Task for abnormal situations, preventing infinite loops if Google Maps has fewer results than requested.
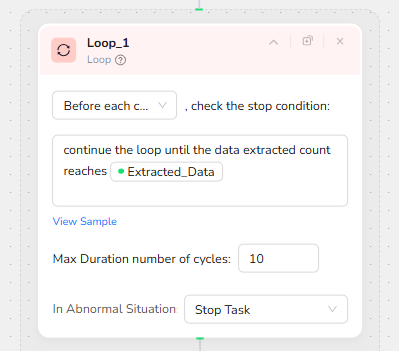
Structured Extraction of Service Provider Data
Inside each loop iteration, the Extract Data node scans the Google Maps results pane and converts each visible listing into structured fields. The Data Field instructions tell the agent to:
identify service provider entries on the page,
map the business title into the Name field,
extract the phone number into Phone, inserting NoPhone if no number is present,
include rating and other relevant attributes as separate fields.
The extraction is configured on Full Page, ensuring the entire results column is considered rather than just the currently visible viewport.
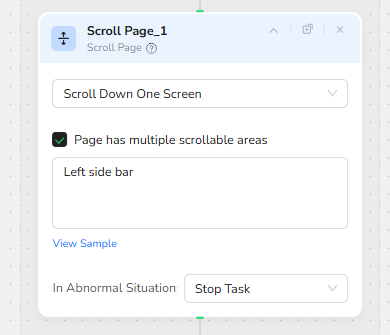
Scrolling to Load Additional Results
To support deep result sets, a Scroll Page node scrolls the left-hand results pane down by one screen at the end of each loop cycle. The option “Page has multiple scrollable areas” is enabled, and the target is specified as the left side bar, which is where the business cards live in the Google Maps UI.
By repeatedly extracting data and scrolling, the workflow can move down through the list and progressively load more businesses until the Extracted_Data target is satisfied.
🤖 Part 2: Automation Integration with Make.com
Overview of the Make Scenario
The Make.com scenario orchestrates the entire conversation flow between the Telegram user, the AI classifier, BrowserAct, and the final response. It listens for incoming Telegram messages, determines whether the message is a valid service request, routes the logic accordingly, calls BrowserAct to retrieve leads, formats the result using Gemini AI, and returns a polished HTML response to the user.
Below is the full Make workflow structure summarizing all routing and automated logic in a single diagram:
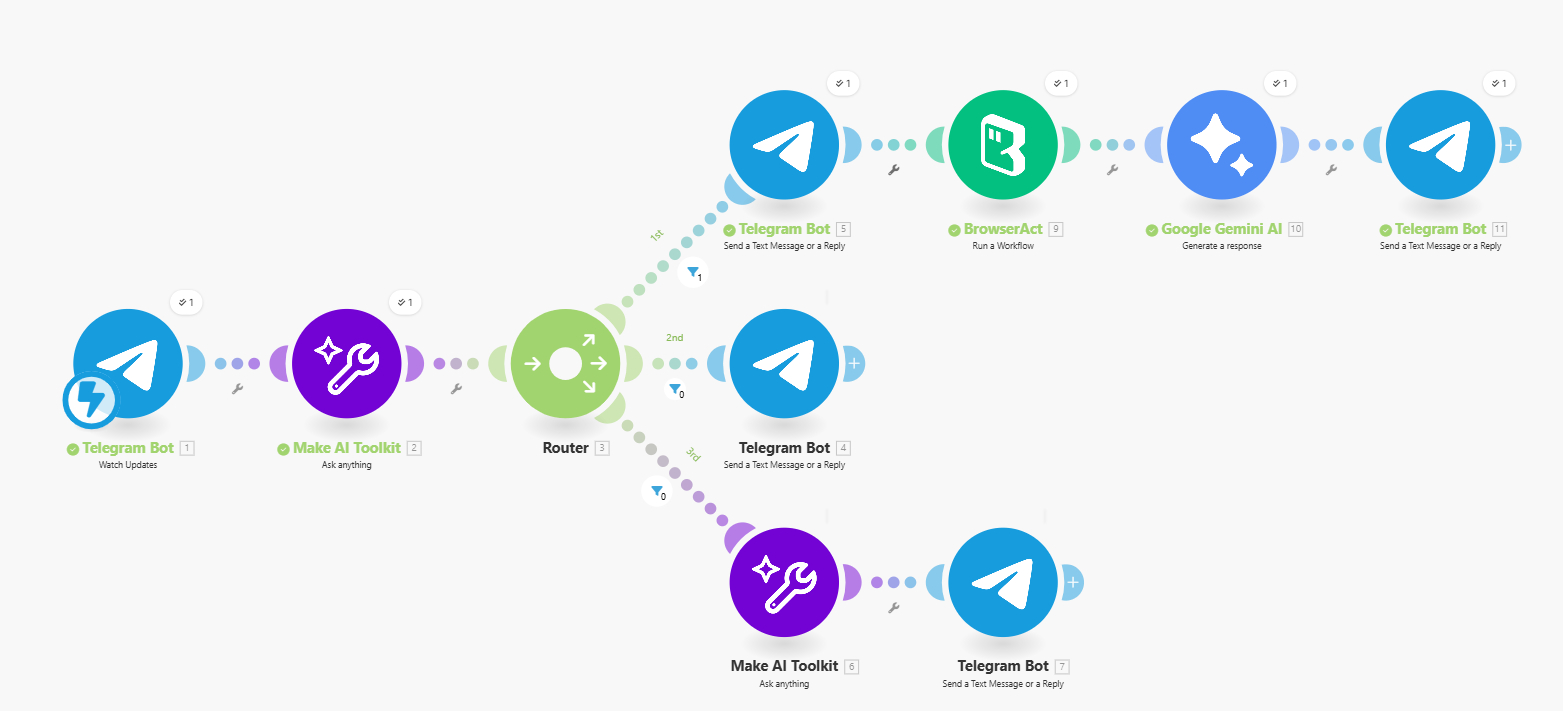
Core Logic Summary
A Telegram Bot module receives the user message.
An AI classifier analyzes whether the message contains both a service and a location.
A Router splits into three paths:
- Complete service request → send a confirmation message, trigger BrowserAct, format the result with Gemini, and send the final provider list back to the user.
- Incomplete request → send a clarification message asking for both service and location.
- Casual chat → generate an AI-based reply and return it to the user.
This streamlined routing ensures the bot behaves intelligently regardless of whether the user is chatting casually or requesting actionable service recommendations.
✨ Applicable Scenarios (Use Cases)
On-Demand Local Service Matching
Users can quickly find plumbers, electricians, cleaners, or any other local service by asking the Telegram bot in natural language.
Customer Support Triage for Property Managers
Property management teams can plug this bot into internal chat workflows to instantly generate provider options when tenants report issues.
Lead Discovery for Agencies and Brokers
Sales or brokerage teams can compile targeted lists of service providers in specific neighborhoods and use them for follow-up outreach.
Intelligent City-Specific Concierge Bots
By adjusting prompt style and messaging, this same structure can power concierge assistants recommending repair services, clinics, gyms, and more.
