
Article Synopsis Bot
Brief
🎯 Core Function: Automated Article & Webpage Synopsis Bot
This workflow is designed for busy knowledge workers, students, and content-heavy professionals who need to quickly understand long articles or webpages without reading everything themselves. It combines BrowserAct to intelligently load and extract article content, Make.com to orchestrate the Telegram conversation and routing logic, and Gemini AI to transform raw page text into a structured, reader-friendly summary that is delivered directly in Telegram.
🧩 Part 1: BrowserAct Workflow Description
This module performs the automated webpage loading, scrolling, and text extraction required to capture article content before it is summarized by the AI system. The workflow consists of seven main steps, each represented in the corresponding images provided.
Start Node – Workflow Input and Authentication
The workflow begins with the Start node, where the global input parameter Target_Link is defined. This parameter represents the webpage URL received from the automation platform. The Start node is also configured with website authentication options: prompting for credentials on each run and enabling the use of stored credentials when available. This ensures compatibility with both public and login-protected sites. The browser environment settings are also initialized at this stage.
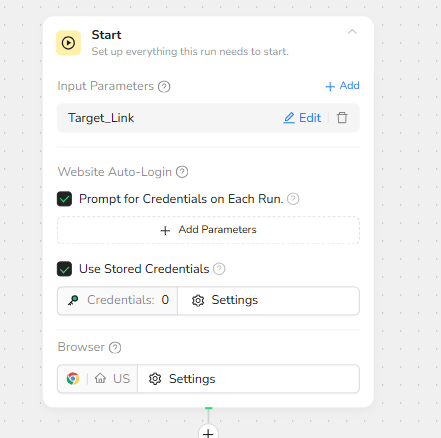
Visit Page – Open Target URL in Browser
The next step is the Visit Page action, which loads the webpage specified by Target_Link. The node is configured to use Current Tab Access so that cookies, sessions, and login states remain consistent throughout the workflow. If the page fails to load, the workflow stops to prevent extraction errors.
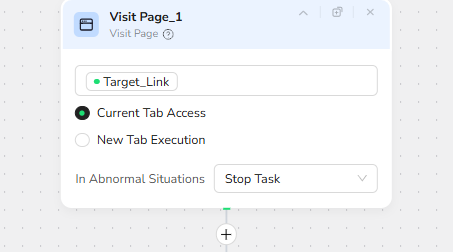
Initial Scroll – Load All Dynamic Content
After the page opens, the Scroll Page action is executed with the Scroll to Bottom option. This forces the page to render all dynamic or lazy-loaded content, ensuring that long articles, images, or infinite-scroll sections fully appear before extraction begins. If scrolling cannot complete, the task stops.
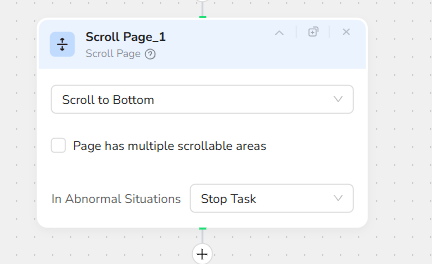
Content Length Evaluation – Determine Extraction Strategy
The Condition node then evaluates whether the page is too long for a single extraction. The question posed is: “Is the page content too long for extraction?” This decision determines which extraction strategy the workflow will use. If the page is long, the workflow will enter a loop-based visible-area extraction method; otherwise, it will perform a single full-page extraction.
Loop Preparation – Long Page Handling
If the condition returns True, indicating a long page, the workflow enters a Loop node. The loop is configured to continue until the end of the page is reached, with a defined maximum number of cycles, such as 10. Before each cycle, the loop checks whether scrolling extensions are still possible. This design prevents infinite loops and ensures a controlled extraction process.
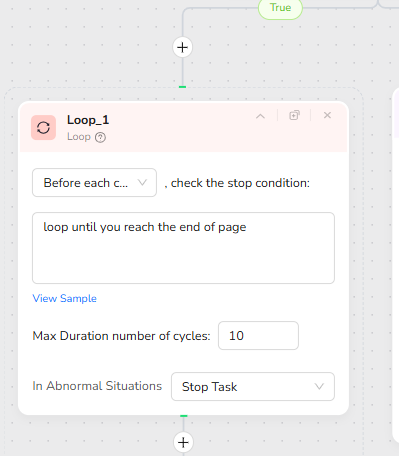
Visible Area Extraction and Progressive Scrolling
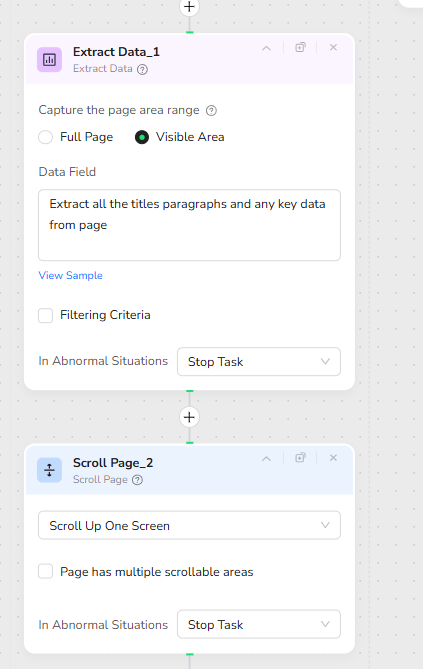
Inside the loop, the Extract Data node captures content only from the Visible Area. The data field instruction reads: “Extract all the titles paragraphs and any key data from page.” This ensures that meaningful text sections are captured progressively. After each extraction, a Scroll Page action is used to “Scroll Up One Screen,” revealing new unseen content for the next cycle. This iterative extract-and-scroll method allows stable extraction of very long pages.
Full Page Extraction for Shorter Pages
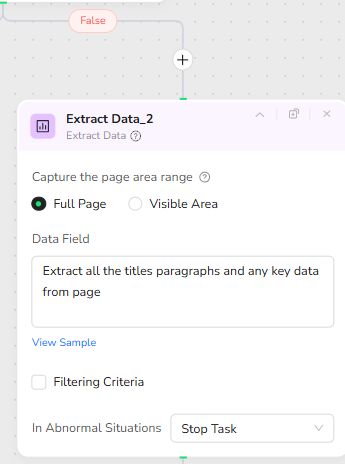
If the condition returns False, indicating that the page is not excessively long, the workflow performs a single extraction using the Full Page mode. The Extract Data node is configured to capture the entire page at once, using the same extraction instruction: “Extract all the titles paragraphs and any key data from page.” This method is faster and more efficient for standard-length articles and static webpages.
🧠 Part 2: Automation Integration with Make.com
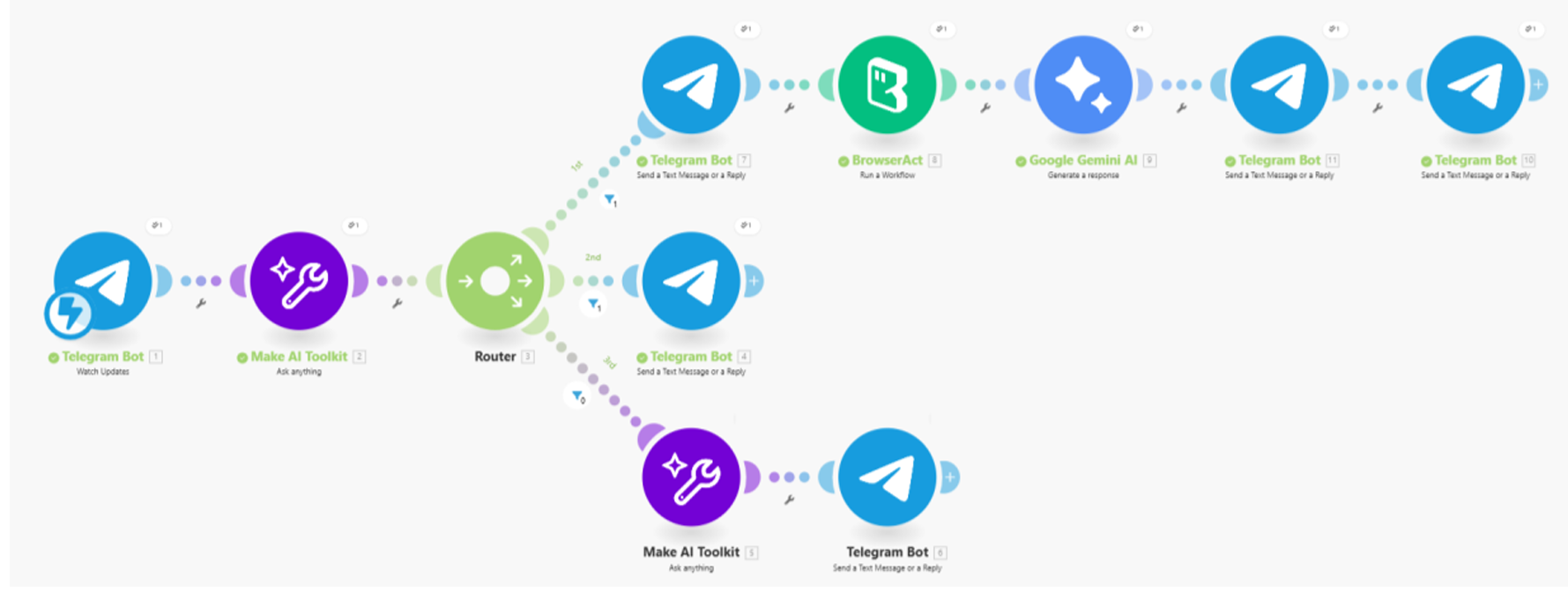
This Make.com scenario manages the Telegram user interaction, determines whether the user message contains a link, and coordinates the BrowserAct and Gemini steps to produce the final summary.
The workflow begins with Telegram Watch Updates, which captures every incoming message. The message is sent to a Make AI Toolkit classifier that identifies three possible intents: casual chat, a summary request with a link, or a request missing a link. The result is routed into three simple branches.
Route 1 handles valid links. The bot sends a short acknowledgment, calls the BrowserAct workflow using the provided URL, and forwards the extracted text to Gemini AI. Gemini transforms the raw content into a structured, mobile-friendly summary using light HTML formatting. The summary is then delivered back to the user through two Telegram messages: one short header and one containing the full summary.
Route 2 handles missing links. If the user asks for a summary without providing a URL, the bot simply responds by asking them to send the link.
Route 3 handles casual chat. If the message has no actionable intent, a Make AI Toolkit module generates a natural conversational response, allowing the bot to behave like a friendly assistant when not summarizing content.
This streamlined structure keeps the logic easy to maintain while providing a polished user experience.
✨ Applicable Scenarios (Use Cases)
News Article Digest: Users can forward news links directly from their browser or other apps into Telegram, receiving structured summaries that highlight key points, analysis, and a bottom-line takeaway.
Research and Learning Companion: Students and knowledge workers can send long-form essays, blog posts, or research explainers to quickly understand the core ideas and suggested next steps without reading every paragraph.
Productivity and Knowledge Inbox: Professionals can drop multiple links into a dedicated Telegram chat throughout the day and later skim the AI-generated summaries instead of opening each site individually.
Accessibility and Focus Aid: For users who struggle with long text, this workflow converts dense webpages into scannable, emoji-enhanced summaries that are easier to digest on mobile devices.
